Authors: Claudia Bortolussi; Dr. Beatrice Schär
Securecell AG / BBraun Medical Care AG, March 2021
Keywords: Seraccess, automatic glucose measurement, method comparison
Background
Securecell’s SeraMaster device is designed to measure blood glucose using the intravenous path. It has already been tested in a laboratory environment, using blood from voluntary blood donation. In this work, we go one step further and evaluate the SeraMaster in a clinical environment. This enables us to test a real-case scenario and estimate the performance over the expected physiological blood glucose range.
Study Design
The clinical study has been carried out at BBraun Medical Care AG, Oerlikon. It contains five 6-hour measurement sessions from five different subjects, all in good health. During each measurement session, blood samples are collected every 15-20 minutes. To cover a wide glucose spectrum, the subjects are given 75 grams of glucose at the beginning of the measurement. After two hours, the subjects are given a glass of orange juice, after two more hours lunch. The glucose level in each sample is measured with the SeraMaster and with YSI for reference.
Results
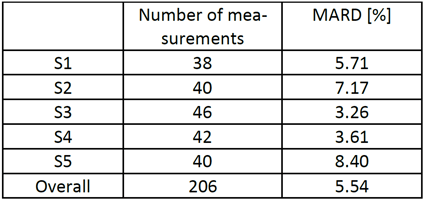
The blood glucose measurement accuracy is evaluated in terms of mean absolute relative difference (MARD):
The first of the figures below presents the SeraMaster and YSI glucose values for one 6-hour measurement. Even during periods of fast glucose variation, the the SeraMaster accurately tracks the reference values.
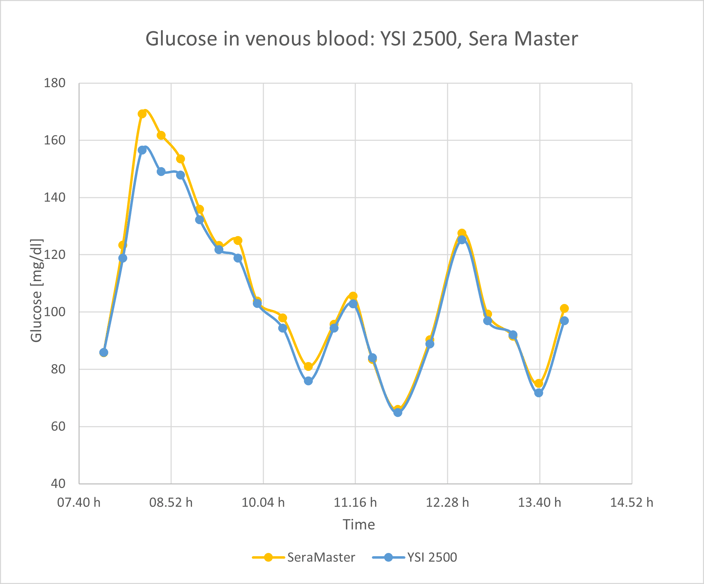
SeraMaster and YSI glucose values
The second figure displays the reference YSI measurement on the horizontal axis and the SeraMaster bias on the vertical axis. 202 out of 206 measurements (98.1%) are in the ±12 mg/dl ±12% error interval*, depicted with solid black lines.
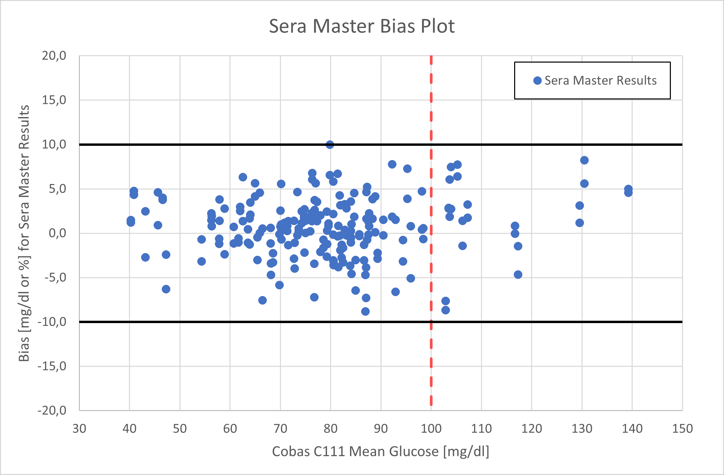
YSI reference measurement (horizontal axis) and SeraMaster bias (vertical axis)
Next steps
This study involved only non-diabetic subjects. The natural next step is to evaluate the SeraMaster accuracy in subjects with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, complementing the SeraMaster with an insulin calculator would lead to an automated insulin delivery mechanism.
| The clinical study shows that the SeraMaster is a reliable, low-error method to measure blood glucose, with MARD = 5.54%. For reference, competitor venous or arterial blood glucose measuring devices report MARD values between 6.5% and 20%. Competitor sub-cutaneous glucose measuring devices report MARD values between 8.5% and 20%. |




